
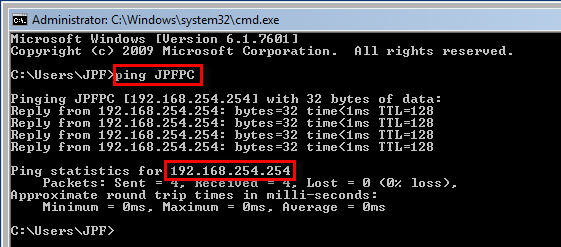

This might be helpful if you wanted to have a number of different web servers running locally on port 80 for some reason. You might also use it for things like: Simulating a large number of different computers in a fast network (simply bring up more interfaces and bind services to them) without using virtual machines. When a process creates a packet with a destination address as loopback address, the operating system loops it back to itself directly without having to go through any NIC. These loopback IP addresses are managed entirely by and within the operating system and enable testing of communications in client-server architecture systems on a single machine. Not exposed to the external network, so they are safe.In IPv4 the range 127.0.0.0 – 127.255.255.255 is reserved for loopback, i.e.We can test network applications with a single box.Network applications can communicate with each other over an operating system without any special hardware.Can check network modules in the operating system without having a network interface card.What are the Advantages of loopback addresses? Any application can bind on these addresses and many send/receive data. The ping is getting a reply, which means loop bac addresses 127.0.0.1 and::11 are active. The following example shows how we can check the status of addresses. For IPV4 Linux have ping and for IPv6 it has ping6 commands. We can use the ping command to check if loopback addresses are active.

IPV4 LOOPBACK ADDRESS HOW TO
::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6 How to check if loopback addresses are working? #vim /etc/hostsġ27.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4 TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0Ĭheck associated domain names. In the output, you can see a “lo” interface. There is a command ( ifconfig) in Linux, which you can use along with the option “-a”, to display the interfaces. In this tutorial, we are using Linux operating system to demonstrate the example. In an operating system, there are commands and utilities to list the IP addresses. How to check the loopback address and associated domain names? For IPv6 the loopback address is ::1, and the domain name is localhost6.For IPv4 the loopback address is 127.0.0.1 the domain name is localhost.The loopback addresses are mapped to the “ lo” interface.
IPV4 LOOPBACK ADDRESS SOFTWARE
This is a software interface that does not have any associated network hardware. What are the loopback addresses for IPv4 and IPv6?Īn operating system has a loopback interface named “ lo”. Each address is 16 bytes long, so a total of 2^128 are possible addresses with the IPv6 address scheme. IPv6 is a newer version with a much larger IP address space. At the start of the internet, the number looks pretty good to hold the IP addresses of all devices worldwide.īut this range will not be sufficient as the number of devices increasing day by day, mainly after the Internet Of Things (IoT) came into the picture.
You can have a maximum of 0xFFFFFFFF number of values. IPv4 is the older version, where each address value is four bytes long. The IPv4 and IPv6 are the versions of the network addresses. If a network client program sends a packet to the loopback address, the operating system routes the packet back to the userspace.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
